2. 山东单县中心医院, 山东 单县 274300
2. Shanxian Central Hospital, Shanxian 274300, Shandong, China
鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤(sinonasal inverted papilloma,SNIP)是一种黏膜上皮源性肿瘤,占鼻腔鼻窦良性肿瘤的首位,国外报道其发病率为0.5%~4.0%,50~70岁男性发病率最高[1, 2]。SNIP在组织学上虽属于良性肿瘤,但复发率高且有潜在恶变的可能,故为临床所重视[3]。近年来随着鼻内镜技术的发展,鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤的鼻内镜手术治疗得到广泛应用。鼻内镜下彻底切除肿瘤的关键在于对其根蒂起源的处理,而术前精确的影像学分析评估对鼻内镜手术一次性彻底切除肿瘤、防止术后复发至关重要[4, 5]。本研究回顾性分析47例经病理组织学证实的鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤CT影像学资料,旨在探讨鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤起源的CT影像学特点。
1 资料与方法 1.1 一般资料收集2013年6月至2015年5月在青岛大学附属医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科就诊,并经手术和病理证实的鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤患者47例为研究对象。其中男28例,女19例,20~85岁,平均54.6岁。主要临床表现包括:鼻塞45例,流涕43例,涕中带血13例,嗅觉减退31例,头痛24例,鼻出血14例,面部麻木9例,耳鸣4例,溢泪1例。病程为1个月~10年。
1.2 影像学资料47例术前均使用美国GE公司生产的Light Speed 16层螺旋CT扫描仪行轴位和冠状位平扫,轴位扫描范围从眉弓至上颌窦底部,冠状位扫描范围从鼻前庭至后鼻孔;扫描层厚为3~5 mm,图像窗宽1 000 HU,窗位200 HU,扫描条件为120 kV,200 mA。观察鼻腔鼻窦的骨质增生情况,局部偏心性骨质密度增高阳性表现可预测鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤根蒂部位(图 1),均匀的、弥漫性骨质增生为非阳性表现。
|
图1 左侧上颌窦后外侧壁可见局部骨质增生隆起 Fig. 1 Local hyperosteogeny was seen on posterolateral wall on the left maxillary sinus |
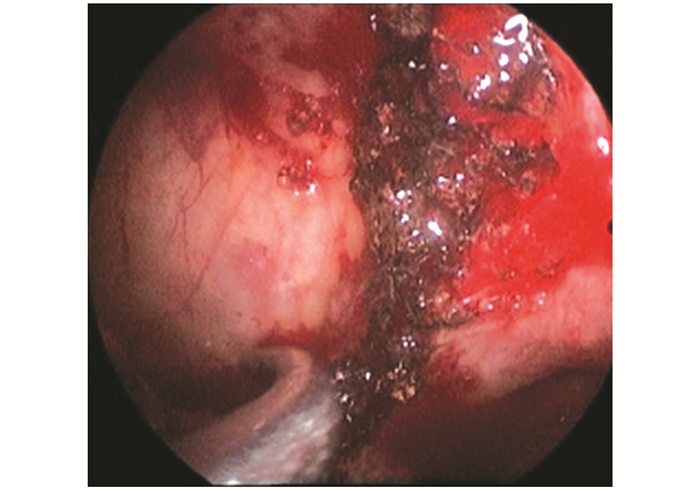
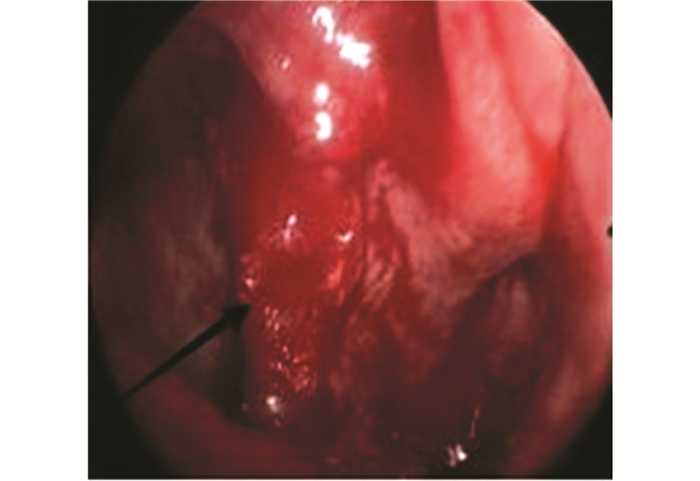
患者均在全身麻醉下行鼻内镜手术,手术均由副主任医师以上完成。首先用1‰肾上腺素棉片收缩鼻腔黏膜,用切割吸引器切除大部分肿瘤组织,术中仔细探查肿瘤来源,寻找肿瘤根蒂所在部位,重点切除根蒂处的肿瘤组织,根蒂周围的黏膜也尽可能切除,使用电钻磨除根蒂周围增生的骨质至正常骨壁(图 2、3)。术中观察肿瘤的根蒂部位,与术前CT影像中的骨质改变阳性表现进行对比,比较两者的一致性。

|
图2 肿瘤的根蒂位于上颌窦口(黑色箭头) Fig. 2 Tumor pedicle located on maxillary sinus (black arrow) |
|
图3 经电刀反复烧灼处理后的肿瘤根蒂部位 Fig. 3 Tumor origin site burned by electric knife was shown |
47例中,术中发现肿瘤根蒂位于鼻腔外侧壁30例,上颌窦10例,筛窦7例。CT影像表现为阳性骨质增生者39例,骨质增生位于鼻腔外侧壁者28例,位于上颌窦者7例,位于筛窦者4例。其中骨质增生阳性CT表现与术中所见肿瘤根蒂部位一致者37例,一致率达78.7%;骨质增生与肿瘤根蒂部位不一致者2例,患者肿瘤根蒂位于前组筛窦,而CT影像显示骨质增生位于鼻甲前端。
3 讨 论鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤是鼻科良性肿瘤之一,其临床特征是生长方式呈缓慢膨胀性、术后复发率高、多次术后有潜在恶变的可能,与鳞状细胞癌发生相关[1, 6]。近年来研究发现,鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤的高复发率主要与鼻内镜手术切除不彻底,特别是肿瘤起源部位的肿瘤残留有关。术后肿瘤复发的部位常在肿瘤根蒂的位置,肿瘤切除不彻底可使复发率达43%,恶变率达10%[7, 8],而首次手术切除彻底的患者则很少复发[9]。因此,对于鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤患者术前根据CT影像学特点明确判断肿瘤的根蒂起源,有助于制定合适的手术方式和手术入路,对鼻内镜术中一次性彻底切除肿瘤和防止术后复发恶变具有非常重要的意义。
鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤在CT上均表现为单侧鼻腔和(或)鼻窦密度较均匀的灰色软组织影,多以鼻腔外侧壁-中鼻道区为中心呈膨胀性生长,鼻腔、上颌窦及筛窦最常被累及,病变周围的骨质多出现移位、吸收破坏等改变,其中病灶呈膨胀性生长、边缘呈乳头状改变、小气泡征、骨质增生硬化及吸收破坏或移位、上颌窦口扩大为鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤较典型的CT特征[10]。鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤的骨质增生改变多为局限性、偏心性,与慢性鼻窦炎等导致的骨质增生表现形式不同,文献报道其特有的局限性、偏心性的骨质增生改变可能与肿瘤发生中一定量炎症细胞的作用相关,肿瘤根蒂部位发生骨炎性改变,在破骨与成骨相互作用下,表现为局部骨质增厚和新骨形成,较小的根蒂起始部位承受较大肿瘤的附着,导致附着处局部高度血管化,从而刺激骨质生长[12, 13]。
目前,准确判断鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤的根蒂起源部位仍需在鼻内镜术中仔细观察,仅仅凭借术者经验判断远达不到组织学彻底切除的要求。随着医学影像技术的发展,有研究表明,根据CT影像中局部骨质增生变化可预测肿瘤根蒂部位,对肿瘤的起源部位可能有提示作用。Lee等[14]研究结果显示,术中鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤根蒂位于鼻腔外侧壁占52.6%,上颌窦占25.0%,前组筛窦占21.1%,蝶窦占6.6%,额窦占6.6%,鼻中隔占2.7%,后组筛窦占2.7%,与CT影像中骨质增生改变位置的一致率高达89.1%。叶菁等[15]术中发现,鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤始发部位最常见于鼻腔外侧壁(46.4%),其次为上颌窦(25.0%)、筛窦(21.4%),而位于额窦及蝶窦者则分别占3.6%,CT影像骨质增生与术中判断的肿瘤始发部位有很高的吻合度(71.4%)。本组病例中鼻内镜术中发现肿瘤根蒂位于鼻腔外侧壁30例,上颌窦10例,筛窦7例。CT影像表现为阳性骨质增生者39例,骨质增生部位位于鼻腔外侧壁者28例,位于上颌窦者7例,位于筛窦者4例。其中骨质增生阳性表现与术中所见肿瘤根蒂始发部位一致者37例,二者的一致率达78.7%,证实了根据CT中骨质增生表现可以预测肿瘤根蒂部位的观点。本组病例中有2例骨质增生与肿瘤根蒂部位不一致,这2例患者肿瘤根蒂位于前组筛窦,而CT影像显示中鼻甲前端的骨质增生,提示中鼻甲的骨化对预测鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤的始发位可能会出现假阳性。推测这可能与该解剖结构易受炎症影响致骨化发生率高有关。
综上所述,CT影像中局部的偏心性骨质增生与鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤根蒂发生密切相关,二者具有较高的一致性,这有助于术前准确评估肿瘤起源和指导手术者制定合理的手术方案,从而彻底切除肿瘤,降低术后复发率和恶变率。
| [1] | Choi J W, Kim S G, Kim Y M, et al. Clinical and histologicfeatures of inverted papilloma-associated malignancy[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2012, 14(32):2349-2354.( 2) 2) |
| [2] | 房高丽,王成硕,张罗.鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤起源部位的影像学研究进展 [J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2014,28(23):1902-1906.FANG Gaoli, WANG Chengshuo, ZHANG Luo. Prediction of the original location of sinonasal invertedpapilloma by preoperative imaging[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg(Chin), 2014, 28(23):1902-1906.( 1) 1) |
| [3] | 梁青壮,李德志,徐震纲, 等.鼻腔-鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤临床及其相关研究进展[J].中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2015, 21(1):80-84.LIANG Qingzhuang, LI Dezhi, XU Zhengang, et al. Clinical and research progress of nasal-paranasal sinuses papilloma[J]. Chin J Otorhinolaryngol Skull Base Surg, 2015, 21(1):80-84.( 1) 1) |
| [4] | Ulkumen B, Kaplan Y, Kıroglu A F, et al. Pediatric invertedpapilloma of the middle ear: case report and review of the literature[J]. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolarygology Extra, 2014, 9(3):1037-1041.( 1) 1) |
| [5] | Eweiss A, Al Ansari A, Hassab M. Invertedpapilloma involvingthe frontal sinus: a management plan[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2009, 266(12):1895-1901.( 1) 1) |
| [6] | 刘晓华,黄雪琨,陈婷婷,等.鼻内翻性乳头状瘤及其肿瘤分级和起源的CT和MRI研究[J].中国现代医生, 2013, 51(18):83-85.IU Xiaohua, HUANG Xuekun, CHEN Tingting, et al. The staging and origin-identification of nasal inverted papilloma using CT and MRI[J]. Chin Modern Doctor, 2013, 51(18):83-85.( 1) 1) |
| [7] | 肖武,刘善凤,王立银,.人类乳头状瘤病毒与鼻内翻性乳头状瘤关系的Meta分析[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2013, 27(11):572-576.XIAO Wu, LIU Shanfeng, WANG Liyin, et al. Meta analysis of the relationship between human papillomavirus and nasal inverted papilloma[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg(Chin), 2013, 27(11):572-576.( 1) 1) |
| [8] | Syrhanen K, Syrjane S. Detection of human papillpma virus in sinonasal papillomas: systematic review and meta- analysis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 30(15):104-115.( 1) 1) |
| [9] | Saha S N, Ghosh A, Sen S, et al. Inverted papilloma: a clinicopathological dilemma with special reference to recurrence and malignant transformation[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2010, 62(4):354-359.( 1) 1) |
| [10] | 于焕新, 刘钢.鼻内翻性乳头状瘤恶变32例临床分析[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2013, 48(12):1002-1005.YU Huanxin, LIU Gang. Malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma: retrospective analysis of 32 cases[J]. Chin J Otorhinol Head Neck Surgery, 2013, 48(12):1002-1005.( 1) 1) |
| [11] | 董怿,周兵,王成硕,等.CT与MRI检查对单侧上颌窦病变的诊断价值[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2013, 48(11):895-900.DONG Yi, ZHOU Bing, WANG Chengshuo, et al. CT and MRI diagnosis of lesions in unilateral maxillary sinus[J]. Chin J Otorhinol Head Neck Surgery, 2013, 48(11):895-900. |
| [12] | Osuch-Wojcikiewicz E, Wojas O, Nyckowska J, et al. Management of recurrent sinonasal inverted papilloma in the experience of ENT department medical university of warsaw[J]. Otolaryngol Pol, 2010, 64(7):73-76.( 1) 1) |
| [13] | Xiao T W, Peng L, Xiu Q W. Factors affecting recurrence of sinonasal Inverted papilloma[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2013, 270(4):1349-1353.( 1) 1) |
| [14] | Lee D K, Chung S K, Dhong H J, et al. Focal hyperos tosis on CT of sinonasal inverted papilloma as a predictor of tumor origin[J]. Am J Neuroradiol, 2007, 28:618-621.( 1) 1) |
| [15] | 叶菁,周文胜,江红群,等.CT中骨质变化对鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤的诊断价值[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 44(2):141-144.YE Jing, ZHOU Wensheng, JIANG Hongqun, et al. Diagnostic value of osseous versity on CT to sinonasal inverted papilloma[J]. Chin J Otorhinol Head Neck Surgery, 2009, 44(2):141-144.( 1) 1) |
 2016, Vol. 30
2016, Vol. 30

