2. 山东大学第二医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 山东 济南 250000 ;
3. 南京军区南京总医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科, 江苏 南京 210002
2. ENT & HN Surgery Department, The Second Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250000, Shandong, China ;
3. Department of Otolaryngology-Head Neck Surgery, Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Command, PLA, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu, China
近年来,我国真菌性鼻窦炎的发病率呈增多趋势[1]。该病有望通过手术获得根治,但真菌性鼻窦炎的术前鉴别诊断较为困难,目前临床上急需一种快速有效的检查方法以帮助临床医生做出术前诊断。现国内外均有采用血浆1-3-β-D葡聚糖检测真菌感染的相关报道[2-3],但对于真菌性鼻窦炎的术前诊断尚无详尽的临床研究。因此,本文设计了前瞻性临床研究,评估血浆1-3-β-D葡聚糖在真菌性鼻窦炎诊断中的价值,以期为此类疾病的术前诊断提供参考。
1 资料与方法 1.1 研究对象本研究通过我院伦理委员会批准, 前瞻性纳入2014年1月至2015年12月在我院收治的鼻窦炎患者。入选标准:①均经病史、临床表现及影像学检查确定有手术指征,并在我院进行手术;②年龄18~70岁;③签署知情同意书。排除标准:①合并有其他部位真菌性感染;②合并有自身免疫性疾病;③肝肾功能障碍;④治疗前3个月内接受激素或其他可能影响免疫功能的药物治疗;⑤合并有恶性肿瘤等终末期疾病。
1.2 研究设计及检测本研究为前瞻性临床研究,入组患者以术后病理诊断为标准分为观察组(真菌性鼻窦炎)和对照组(细菌性鼻窦炎)。入院后1~2 d及术后1~2周分别采集静脉血,离心后取血浆(3 000 r/min离心3 min),-80 ℃冻存。采用ELISA法分别检测1-3-β-D葡聚糖(Associates of Cape Cod,USA)、CRP(R&D,USA)、白介素-10(Interleukin-10,IL-10; R&D,USA)及PCT(R&D,USA)。
1.3 观察指标比较2组一般临床资料;分别比较2组术前、术后血浆1-3-β-D葡聚糖、CRP、IL-10及PCT的改变;分析各项检测指标间的相关性;评估各项检测指标对真菌性鼻窦炎的诊断价值。
1.4 统计学处理数据采用SPSS 23.0软件进行统计分析。计量资料以x±s表示,采用t检验。率的比较使用卡方检验。相关性分析采用Pearson检验。各项检测指标对真菌性鼻窦炎的诊断价值采用受试者工作曲线(ROC)分析。检验水准为α=0.05,P<0.05定义为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果 2.1 一般资料本研究共纳入符合条件的患者83例,其中观察组41例,对照组42例。观察组中,病理诊断均为曲霉菌感染,其中烟曲霉菌25例,黄曲霉菌16例。2组患者在性别比例、年龄、体质量指数(BMI)、吸烟及饮酒史上比较均无统计学差异(P>0.05)。见表 1。
| 表 1 2组患者一般临床资料的比较 Table 1 Comparison of clinical data between the two groups |
术前,2组血浆PCT、CRP及IL-10水平比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05);观察组术前血浆1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平显著高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。术后,2组患者各项指标比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。治疗前后,2组患者IL-10水平均未发生明显改变(P>0.05);与治疗前比较,2组患者治疗后PCT及CRP水平均显著降低(P<0.05);与治疗前比较,观察组患者1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平显著降低(P<0.05),而对照组无明显改变(P>0.05)。见表 2。
| 表 2 2组患者治疗前后血液学指标的改变 Table 2 Comparison of haematological index between the two groups |
观察组患者术前,烟曲霉菌感染患者与黄曲霉菌感染患者外周血1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平比较差异无统计学意义(19.11±3.53 vs 20.46±2.48;t=1.330,P=0.191);术后2组外周血1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平比较差异无统计学意义(3.14±0.78 vs 3.44±0.14;t=1.325,P=0.193)。
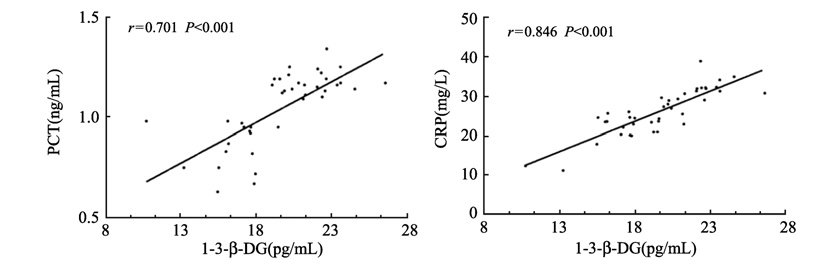
2.3 观察组术前血浆1-3-β-D葡聚糖与其他指标的相关性分析观察组患者术前血浆1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平与PCT(t=0.701,P=0.002)及CRP(t=0.846,P=0.002)均呈现显著正相关,见图 1。
|
图 1 观察组术前血浆1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平与CRP及PCT的相关性 Figure 1 Correlation between the level of 1-3-β-D glucan and CRP and PCT in patients of observation group |
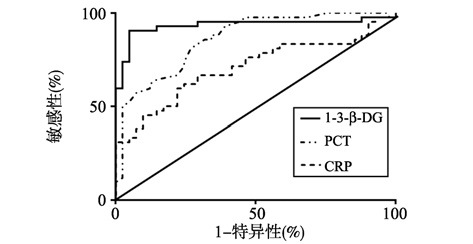
ROC曲线分析显示,当1-3-β-D葡聚糖取值为12.0 pg/mL时对感染的诊断敏感性为90.48%,特异性为95.12%,优于PCT及CPR,见图 2及表 3。
|
图 2 术前PCT、CRP及1-3-β-D葡聚糖对真菌性鼻窦炎诊断价值的ROC曲线 Figure 2 ROC curve of value of preoperative 1-3-β-D glucan,PCT and CRP levels for the diagnosis of fungal rhinosinusitis |
| 表 3 术前1-3-β-D葡聚糖、PCT、CRP检测对真菌性鼻窦炎的诊断价值 Table 3 Value of preoperative 1-3-β-D glucan,PCT and CRP levels for the diagnosis of fungal rhinosinusitis |
真菌性鼻窦炎已然成为耳鼻喉科较为常见的感染性疾病。随着耳鼻喉科手术技术的长足发展,通过手术清除感染灶是根治该病的有效治疗方法。由于部分患者CT影像学表现不典型[4-5],而真菌培养较为耗时且易因污染导致结果不可靠[6-7],使得真菌性鼻窦炎的术前诊断较为困难。因而真菌性鼻窦炎往往难以与一般细菌性鼻窦炎相鉴别,这给手术方案的设计带来了困难[8]。现临床上急需更为简便、可靠的诊断真菌性鼻窦炎的方法。1-3-β-D葡聚糖为真菌细胞壁的主要成分,当真菌侵入人体后可因吞噬细胞的消化作用而释放至外周血[9-10]。因此,1-3-β-D葡聚糖对真菌感染的诊断具有较高的特异性[11]。本课题组前期通过回顾性研究发现真菌性鼻窦炎患者外周血1-3-β-D葡聚糖显著高于鼻息肉、鼻窦炎及鼻中隔偏曲患者,1-3-β-D葡聚糖有望成为真菌性鼻窦炎术前诊断的实验室指标,可以一定程度弥补CT、真菌培养检查的不足[12]。为进一步验证这一结果,同时分析1-3-β-D葡聚糖诊断真菌性鼻窦炎的诊断临界点并与其他血液学指标进行对比,设计了此项前瞻性研究。
本研究发现,鼻窦炎患者术前外周血PCT及CRP均显著高于正常值,但1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平的升高仅见于真菌性鼻窦炎患者,这再一次肯定了回顾性研究的结论。进一步分析真菌性鼻窦炎患者外周血1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平与PCT及CRP的相关性,结果发现,1-3-β-D葡聚糖与CRP及PCT均呈现显著正相关。CRP是一种急性期反应蛋白,常在感染、应激等情况下升高,可一定程度反映患者全身炎症反应的水平[13]。PCT是在细菌、寄生虫、炎症介质等作用于人体神经内分泌细胞或其他特殊类型细胞而分泌的一种蛋白质[14]。外周血PCT水平在严重感染、脓毒症和多器官功能障碍时升高[15]。1-3-β-D葡聚糖与CRP及PCT呈现正相关,提示1-3-β-D葡聚糖可反映真菌性鼻窦炎感染的严重程度,且可一定程度代表CRP及PCT的检测结果。为分析1-3-β-D葡聚糖诊断真菌性鼻窦炎的诊断临界点,使得这一指标更具临床实用价值,采用ROC曲线分析了1-3-β-D葡聚糖对真菌性鼻窦炎的诊断价值,并与PCT及CRP进行比较。结果发现,当取诊断临界值为12.0 pg/mL时,1-3-β-D葡聚糖术前诊断真菌性鼻窦炎的敏感性及特异性均超过90%。提示1-3-β-D葡聚糖是辅助诊断真菌性鼻窦炎的理想指标。
本研究仍有许多不足之处:虽然发现了1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平与CRP及PCT具有正相关关系,但这些指标间的相互影响机制尚需进一步研究以明确,并不能得出1-3-β-D葡聚糖水平可代表疾病严重程度的结论。虽然本研究计算出了1-3-β-D葡聚糖诊断真菌性鼻窦炎的诊断临界值,但由于纳入的真菌性鼻窦炎致病菌均为曲霉菌,加之样本量有限,这一临界值尚需进一步研究以矫正。
综上,本研究证实1-3-β-D葡聚糖对真菌性鼻窦炎的诊断较为可靠,有望成为辅助术前诊断的实用指标。
| [1] |
章晓军, 周剑勇, 谭国鹏, 等.
42例非侵袭性真菌性鼻窦炎临床分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志 , 2013, 19 (2) : 129–131.
ZHANG Xiaojun, ZHOU Jianyong, TAN Guopeng, et al. Clinical analysis of non-invasive fungal rhinosinusitis in 42 cases[J]. Chin J Otolaryngol-skull Base Surgery , 2013, 19 (2) : 129–131. (  0) 0)
|
| [2] |
Hou T Y, Wang S H, Liang S X, et al.
The screening performance of serum 1,3-beta-D-Glucan in patients with invasive fungal diseases:a Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. PLos One , 2015, 10 (7) : e0131602.
DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0131602 ( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
汤小军, 黄建春, 刘航, 等.
检测(1, 3)-β-D-葡聚糖在老年肺癌侵袭性肺部真菌感染中的临床价值[J]. 广西医学 , 2014, 36 (2) : 170–172.
TANG Xiaojun, HUANG Jianchun, LIU Hang, et al. Clinical value of plasma (1, 3)-β-d-glucan detection for invasive fungal infections in aged patients with lung cancer[J]. Guangxi Medical Journal , 2014, 36 (2) : 170–172. (  0) 0)
|
| [4] |
刘少峰, 王文, 伍丽娟, 等.
单侧鼻腔鼻窦病变CT诊断与临床分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志 , 2012, 18 (4) : 307–309.
LIU Shaofeng, WANG Wen, WU Lijuan, et al. CT diagnosis and clinical analysis for unilateral nasal sinus lesions[J]. Chin J Otolaryngology-Skull Base Surgery , 2012, 18 (4) : 307–309. (  0) 0)
|
| [5] |
宋明艳, 李娜, 姜彦, 等.
真菌性鼻窦炎CT影像学的非特征性表现[J]. 山东医药 , 2014, 54 (29) : 93–94.
SONG Mingyan, LI Na, JIANG Yan, et al. Non-distinctive features on CT scan of fungal sinusitis[J]. Shandong Med J , 2014, 54 (29) : 93–94. (  0) 0)
|
| [6] |
Mendes Neto J A, Guerreiro V M, Hirai E R, et al.
The role of maxillary sinus puncture on the diagnosis and treatment of patients with hospital-acquired rhinosinusitis[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol , 2012, 78 (4) : 35–41.
DOI:10.1590/S1808-86942012000400008 ( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
Jain S, Das S, Gupta N, et al.
Frequency of fungal isolation and antifungal susceptibility pattern of the fungal isolates from nasal polyps of chronic rhinosinusitis patients at a tertiary care centre in north India[J]. Med Mycol , 2013, 51 (2) : 164–169.
DOI:10.3109/13693786.2012.694486 ( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
戴勇传, 倪昊生.
非侵袭性真菌性鼻窦炎手术治疗的探讨[J]. 医学理论与实践 , 2013, 26 (20) : 2729–2730.
DAI Yongchuan, NI Haosheng. The treatment of noninvasive surgery for fungal sinusitis[J]. J of Med Theory Prac , 2013, 26 (20) : 2729–2730. (  0) 0)
|
| [9] |
Petraitiene R, Petraitis V, Bacher J D, et al.
Effects of host response and antifungal therapy on serum and BAL levels of galactomannan and (1→3)-β-D-glucan in experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis[J]. Med Mycol , 2015, 53 (6) : 558–568.
DOI:10.1093/mmy/myv034 ( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
Prattes J, Schilcher G, Krause R.
Reliability of serum 1,3-beta- d -glucan assay in patients undergoing renal replacement therapy:a review of the literature[J]. Mycoses , 2014, 58 (1) : 4–9.
( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
Raggam R B, Fischbach L M, Prattes J, et al.
Detection of (1→3)-β-D-glucan in same-day urine and serum samples obtained from patients with haematological malignancies[J]. Mycoses , 2015, 58 (7) : 394–398.
DOI:10.1111/myc.2015.58.issue-7 ( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
余鹏举, 黄媛媛, 江满杰, 等.
血浆1-3-β-D葡聚糖检测在真菌性鼻窦炎诊断中的临床价值[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志 , 2014 (2) : 107–110.
YU Pengju, HUANG Yuanyuan, JIANG Manjie, et al. Diagnostic value of plasma 1-3-β-D glucan assay in fungal rhinosinusitis[J]. Chin J Otolaryngology-Skull Base Surgery , 2014 (2) : 107–110. (  0) 0)
|
| [13] |
Markanday A.
Acute phase reactants in infections: evidence-based review and a guide for clinicians[J]. Open Forum Infect Dis , 2015, 2 (3) : ofv098.
DOI:10.1093/ofid/ofv098 ( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
Davies J.
Procalcitonin[J]. J Clin Pathol , 2015, 68 (9) : 675–679.
DOI:10.1136/jclinpath-2014-202807 ( 0) 0)
|
| [15] |
Carr J A.
Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy for septic patients in the surgical intensive care unit[J]. J Intensive Care , 2015, 3 (1) : 36.
DOI:10.1186/s40560-015-0100-9 ( 0) 0)
|
 2016, Vol. 30
2016, Vol. 30
